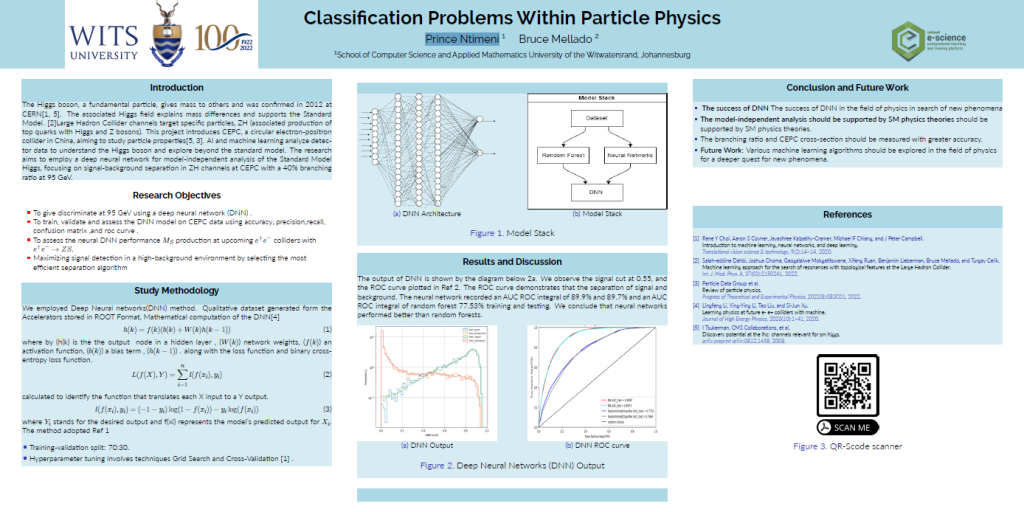
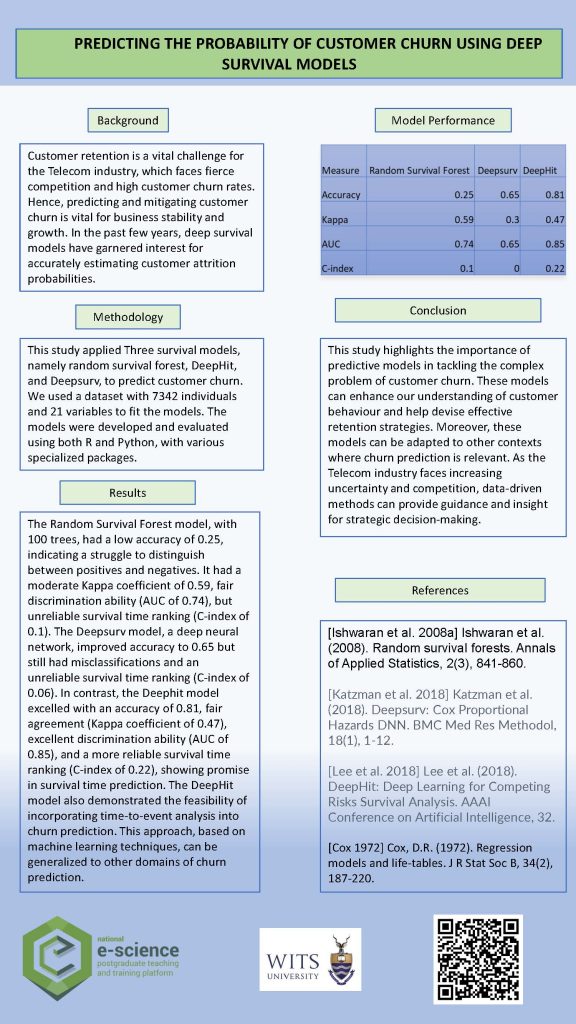
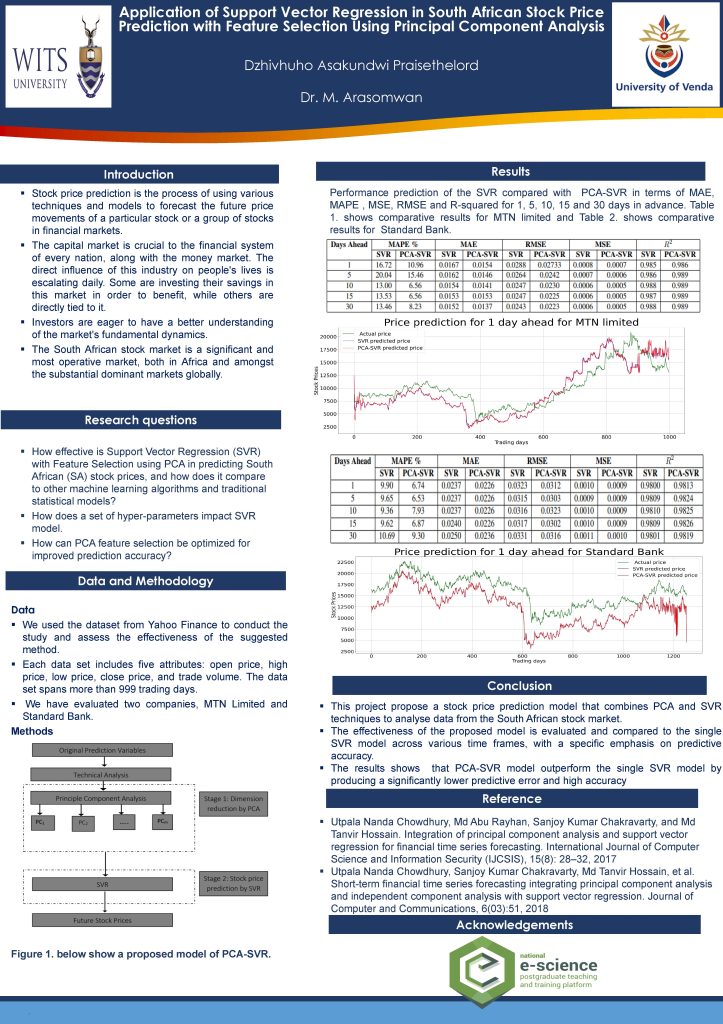
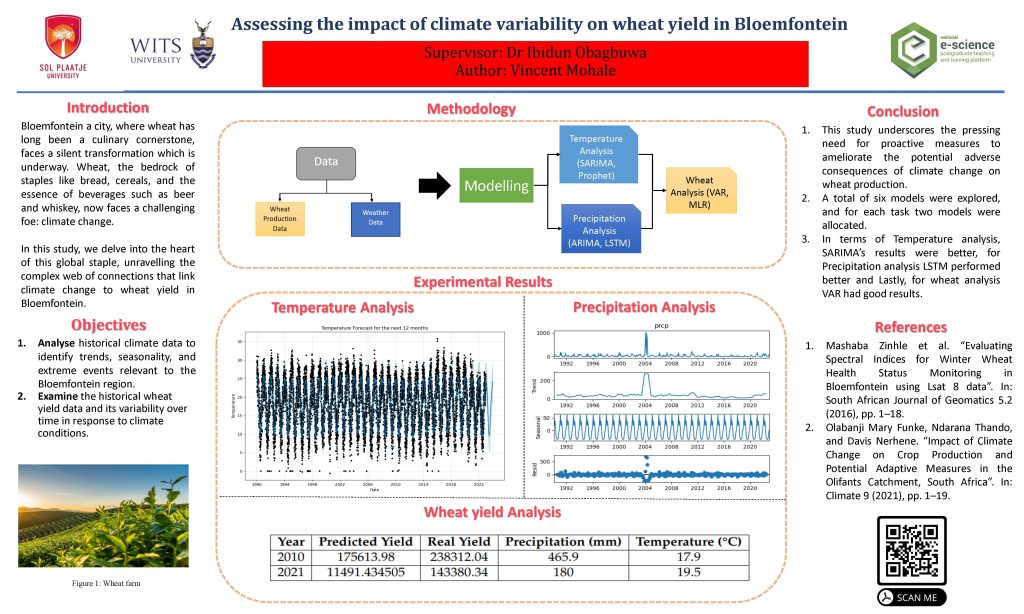
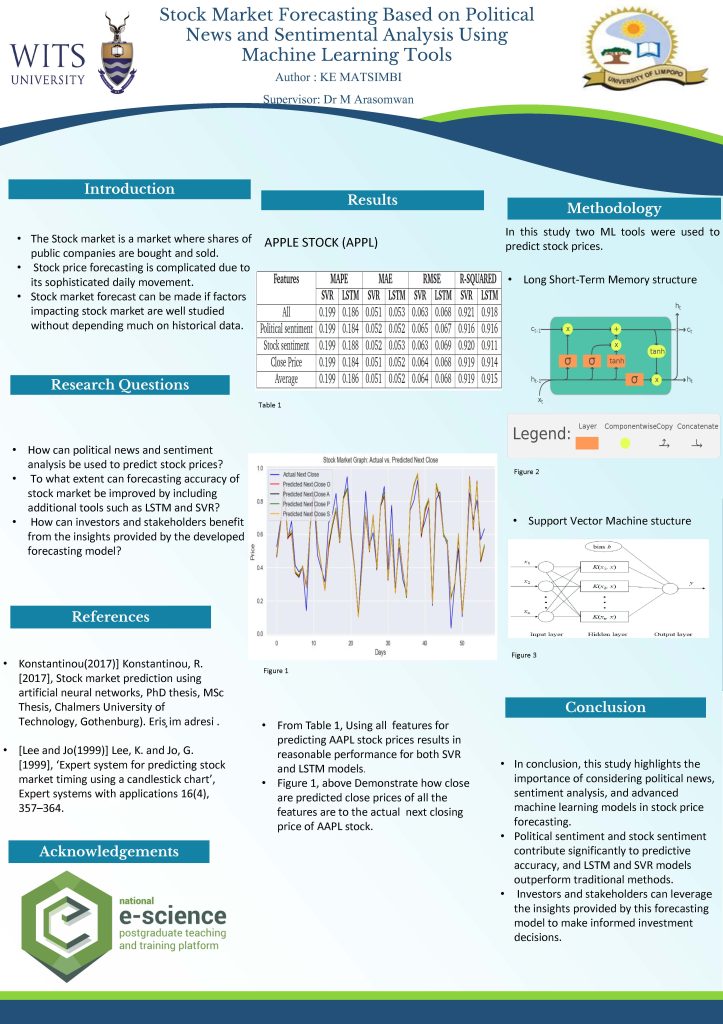
Classification Problems Within Particle Physics
Researcher: Mafanedza Nephawe, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg
Supervisor: Prof Prince Ntimeni
The Higgs boson, a fundamental particle, gives mass to others and was confirmed in 2012 at
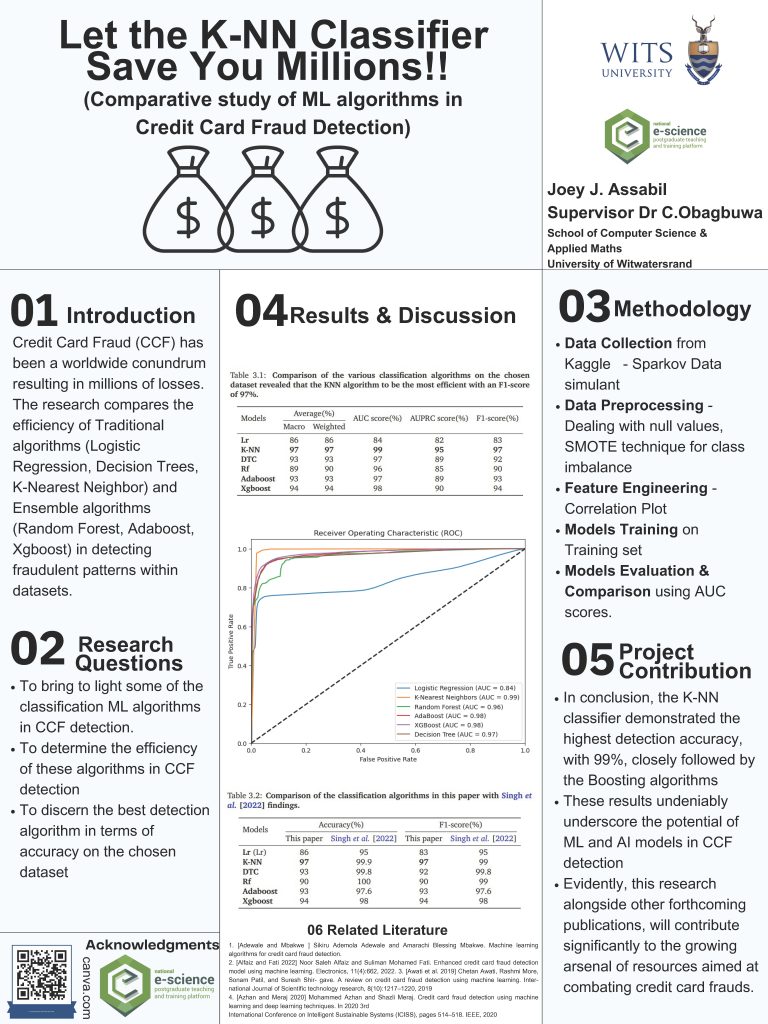
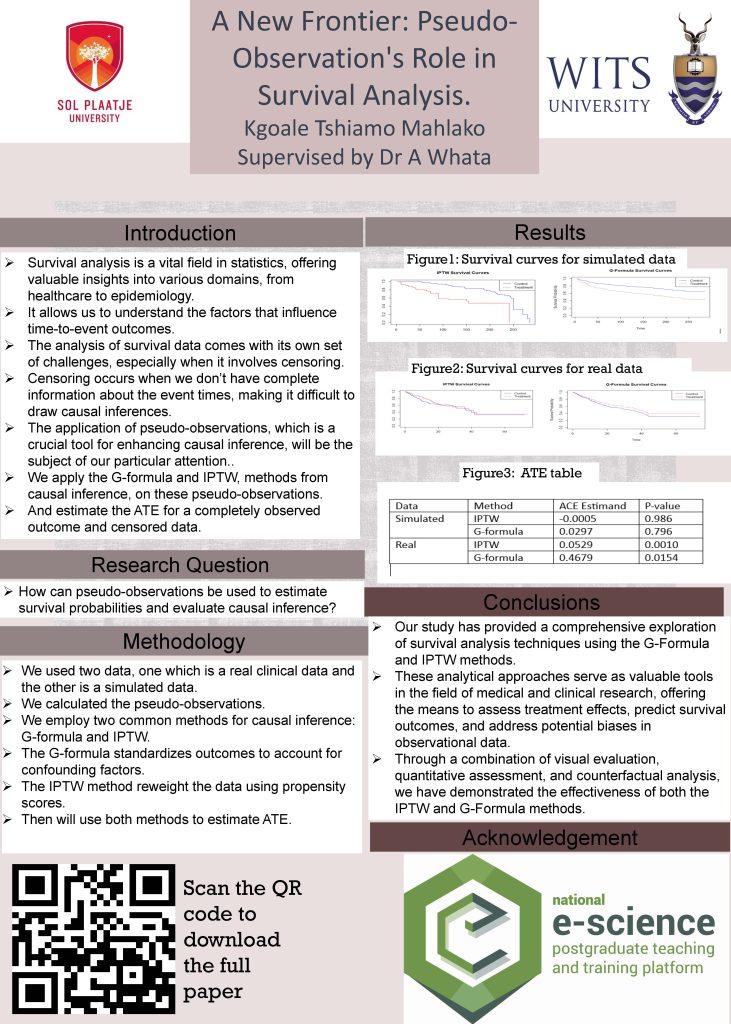
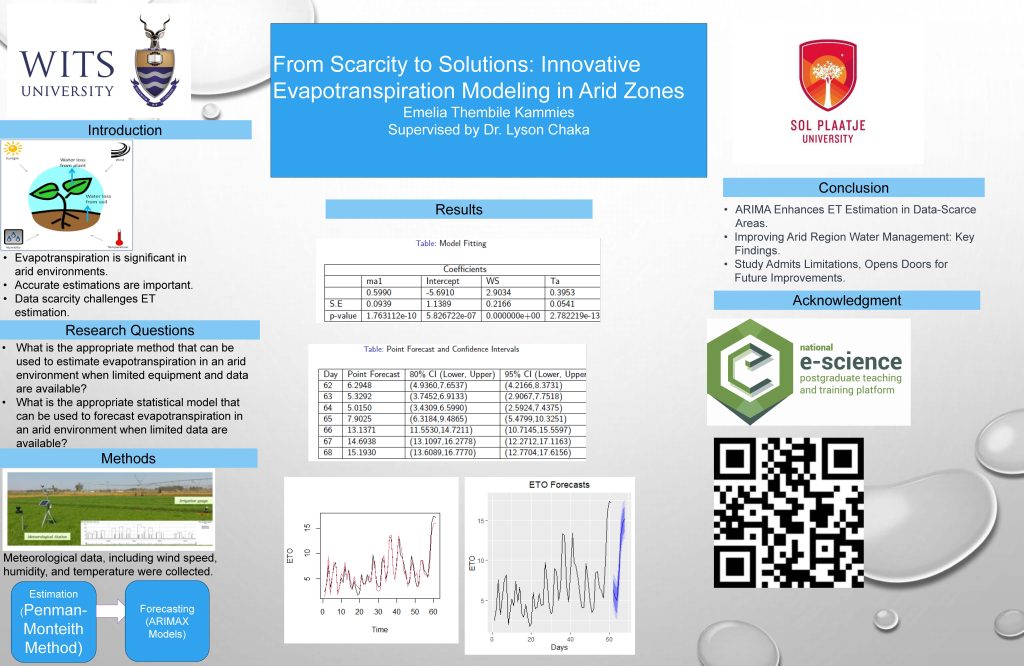
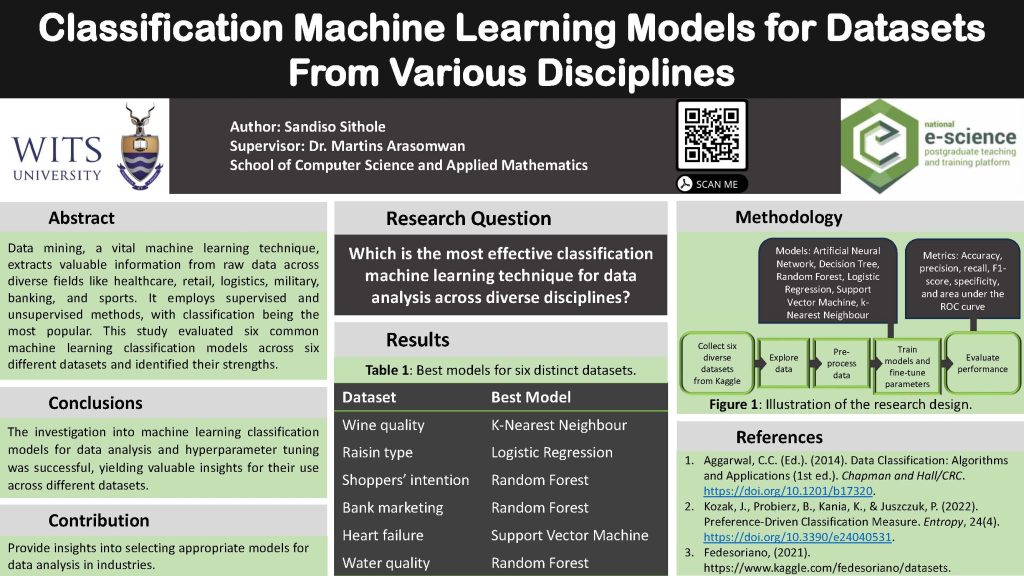
CERN[1, 5]. The associated Higgs field explains mass differences and supports the Standard
Model. [2]Large Hadron Collider channels target specific particles, ZH (associated production of
top quarks with Higgs and Z bosons). This project introduces CEPC, a circular electron-positron
collider in China, aiming to study particle properties[5, 3]. AI and machine learning analyze detector
data to understand the Higgs boson and explore beyond the standard model. The research
aims to employ a deep neural network for model-independent analysis of the Standard Model
Higgs, focusing on signal-background separation in ZH channels at CEPC with a 40% branching
ratio at 95 GeV.