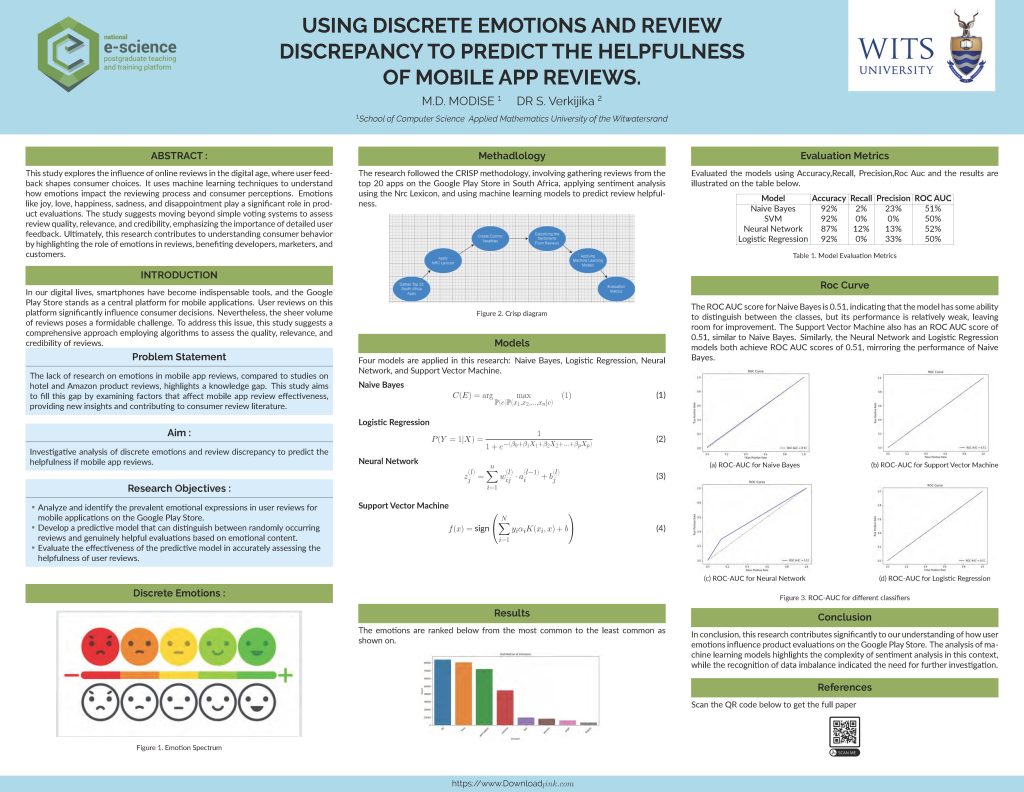
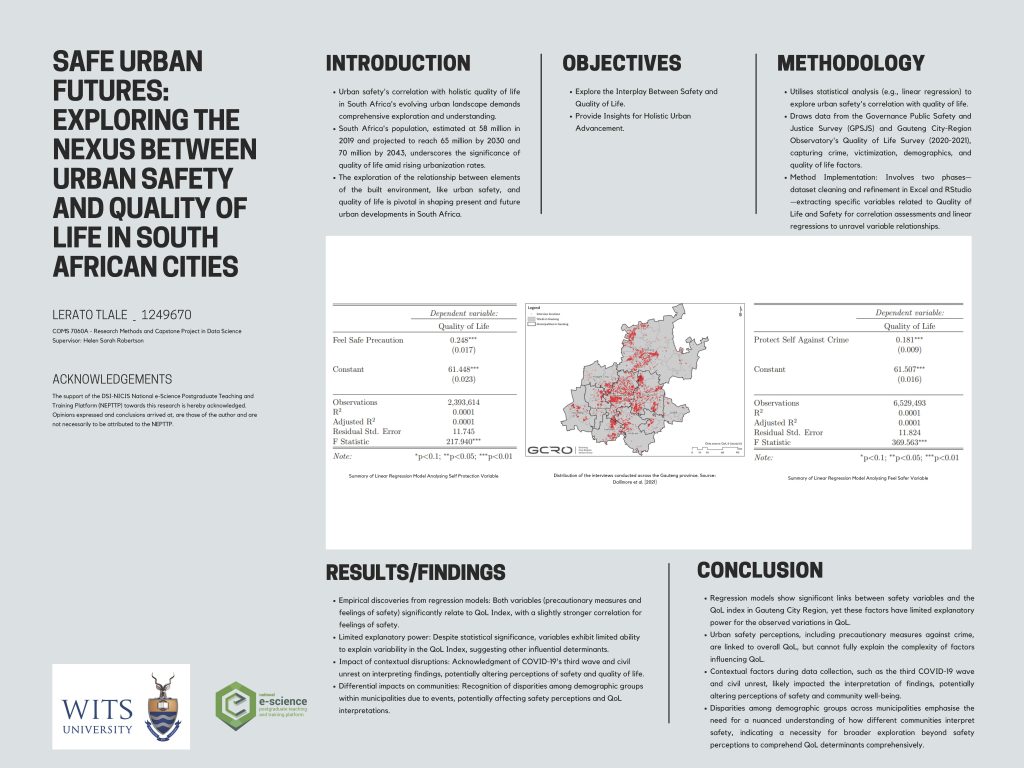
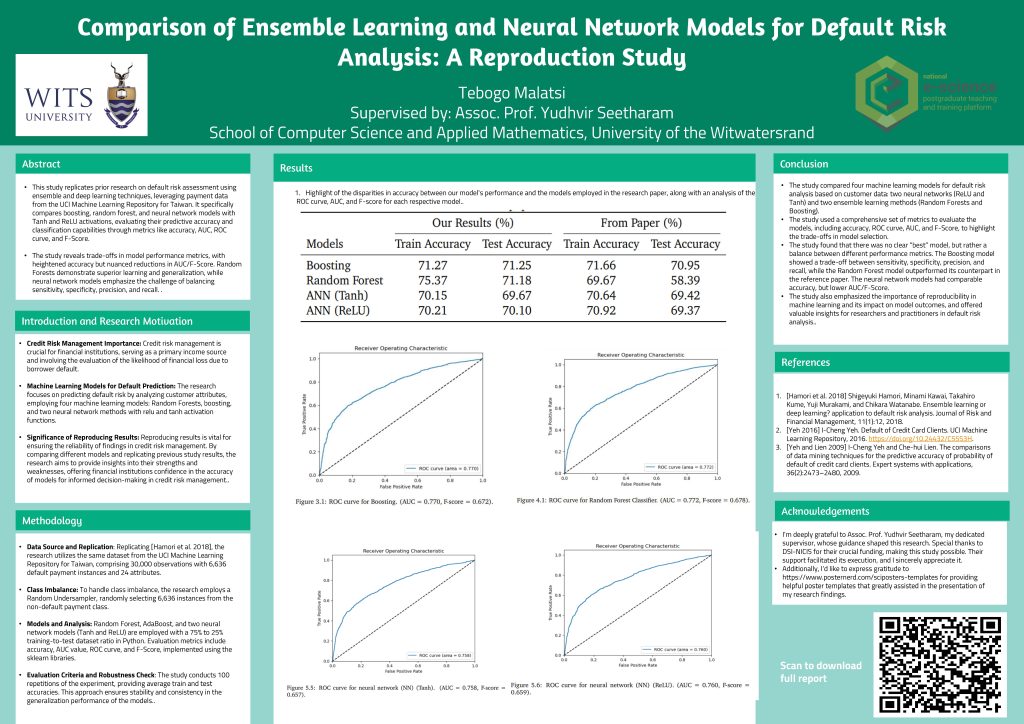
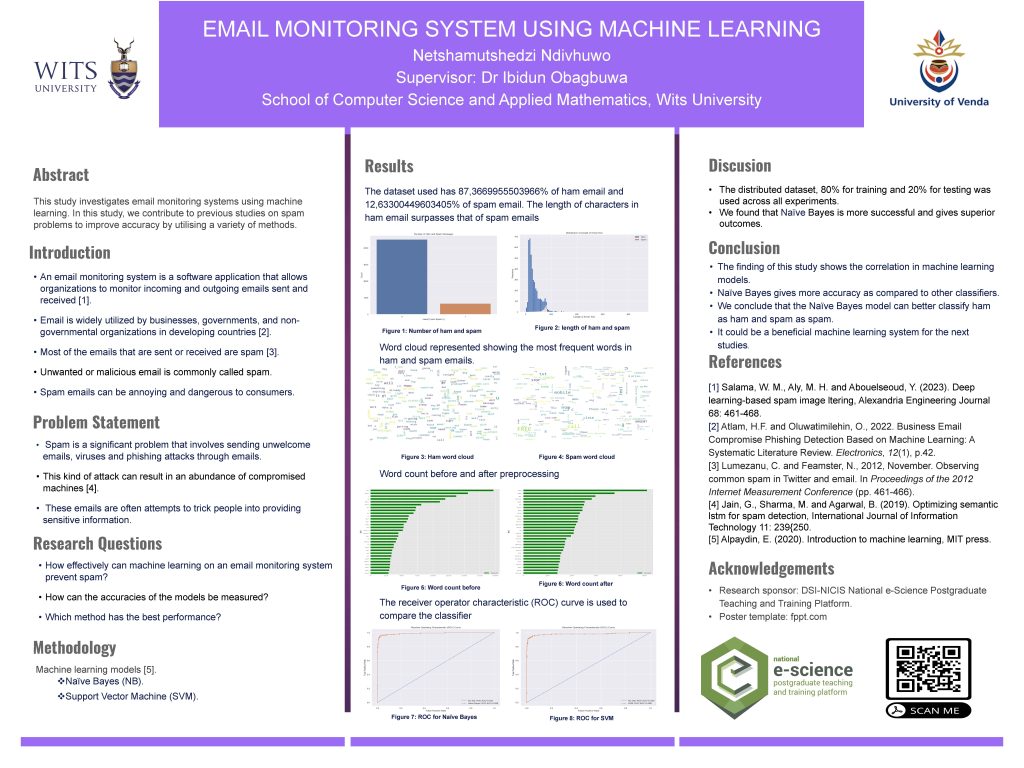
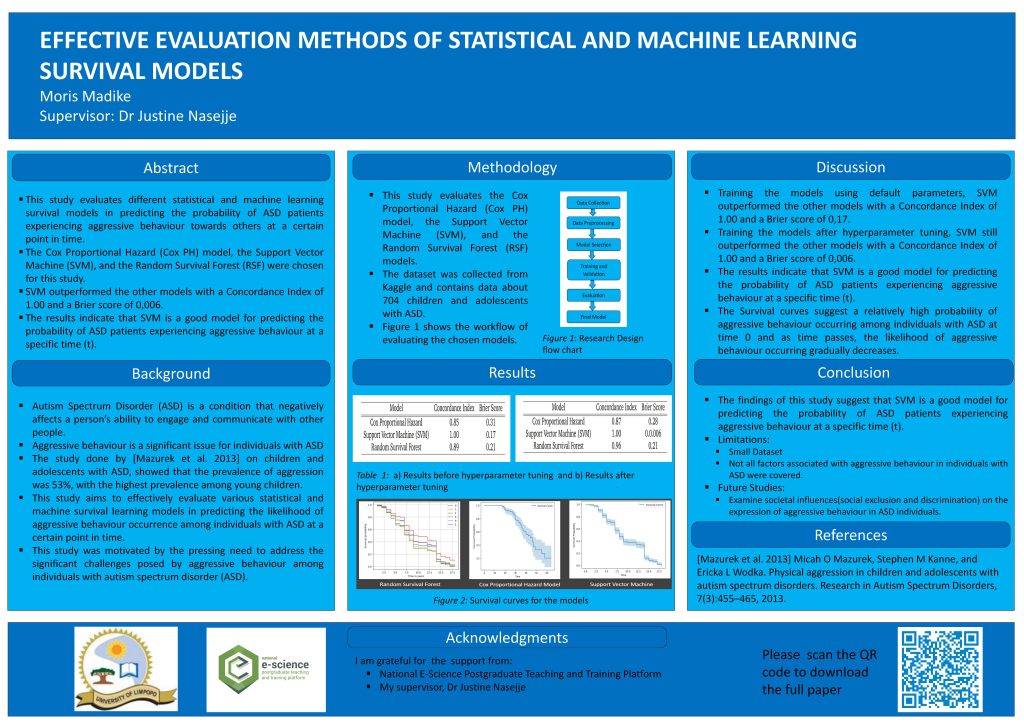
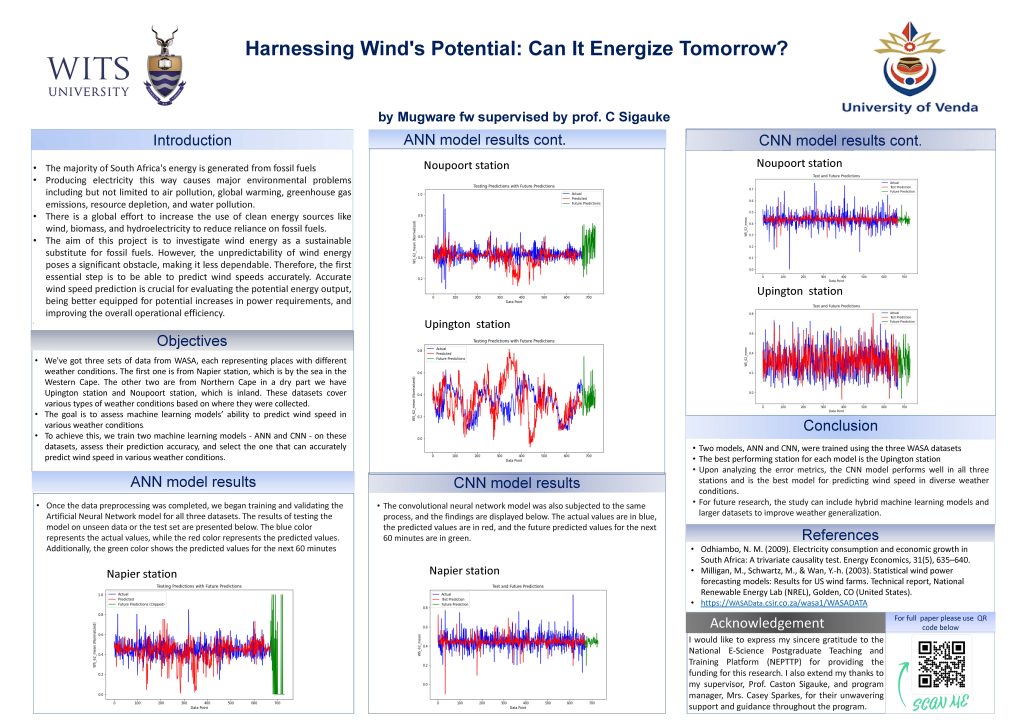
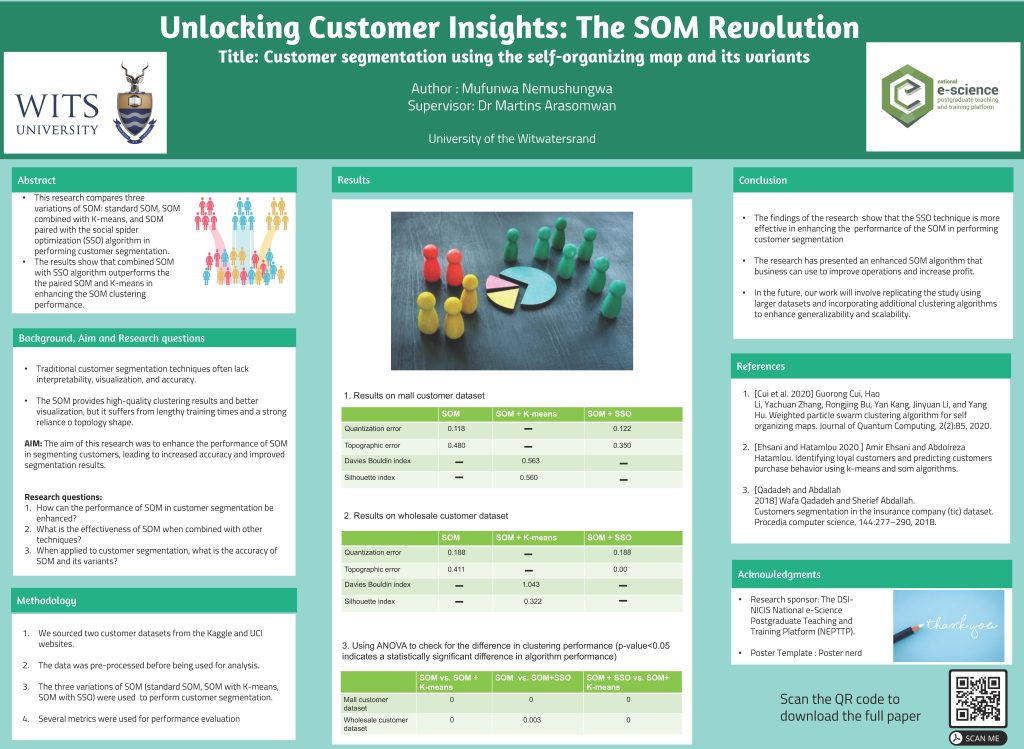
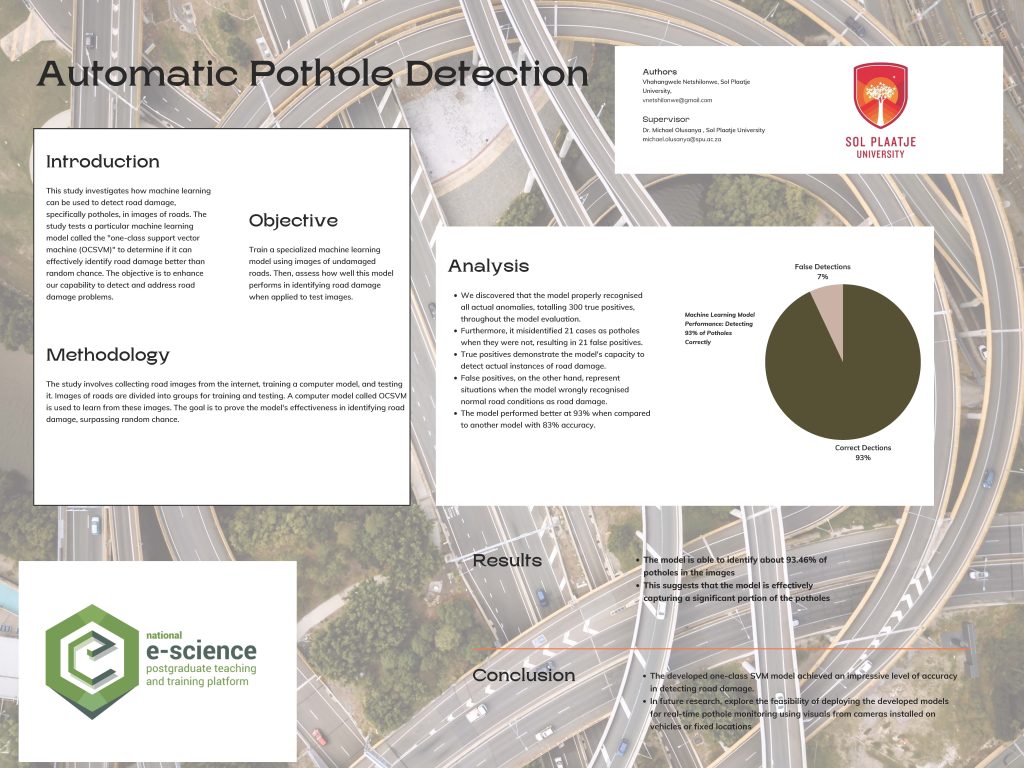
Using discrete emotions and review discrepency to predict the helpfulness of mobile app reviews
Researcher: Mpho Modise, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg
Supervisor: Dr S. Verkijika, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg
In our digital lives, smartphones have become indispensable tools, and the Google
Play Store stands as a central platform for mobile applications. User reviews on this
platform significantly influence consumer decisions. Nevertheless, the sheer volume
of reviews poses a formidable challenge. To address this issue, this study suggests a
comprehensive approach employing algorithms to assess the quality, relevance, and
credibility of reviews.